TIA's Glossary of Telecommunication Terms
0-9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
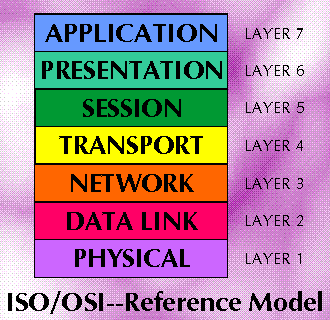
Open Systems Interconnection--Reference Model (OSI--RM)
An abstract description of the digital communications between application processes running in distinct systems. The model employs a hierarchical structure of seven layers. Each layer performs value-added service at the request of the adjacent higher layer and, in turn, requests more basic services from the adjacent lower layer:
- Physical Layer: Layer 1, the lowest of seven hierarchical layers. The Physical layer performs services requested by the Data Link Layer. The major functions and services performed by the physical layer are: (a) establishment and termination of a connection to a communications medium; (b) participation in the process whereby the communication resources are effectively shared among multiple users, e.g., contention resolution and flow control; and, (c) conversion between the representation of digital data in user equipment and the corresponding signals transmitted over a communications channel.
- Data Link Layer: Layer 2. This layer responds to service requests from the Network Layer and issues service requests to the Physical Layer. The Data Link Layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and to detect and possibly correct errors that may occur in the Physical Layer. Note: Examples of data link protocols are HDLC and ADCCP for point-to-point or packet-switched networks and LLC for local area networks.
- Network Layer: Layer 3. This layer responds to service requests from the Transport Layer and issues service requests to the Data Link Layer. The Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source to a destination via one or more networks while maintaining the quality of service requested by the Transport Layer. The Network Layer performs network routing, flow control, segmentation/desegmentation, and error control functions.
- Transport Layer: Layer 4. This layer responds to service requests from the Session Layer and issues service requests to the Network Layer. The purpose of the Transport Layer is to provide transparent transfer of data between end users, thus relieving the upper layers from any concern with providing reliable and cost-effective data transfer.
- Session Layer: Layer 5. This layer responds to service requests from the Presentation Layer and issues service requests to the Transport Layer. The Session Layer provides the mechanism for managing the dialogue between end-user application processes. It provides for either duplex or half-duplex operation and establishes checkpointing, adjournment, termination, and restart procedures.
- Presentation Layer: Layer 6. This layer responds to service requests from the Application Layer and issues service requests to the Session Layer. The Presentation Layer relieves the Application Layer of concern regarding syntactical differences in data representation within the end-user systems. Note: An example of a presentation service would be the conversion of an EBCDIC-coded text file to an ASCII-coded file.
- Application Layer: Layer 7, the highest layer. This layer interfaces directly to and performs common application services for the application processes; it also issues requests to the Presentation Layer. The common application services provide semantic conversion between associated application processes. Note: Examples of common application services of general interest include the virtual file, virtual terminal, and job transfer and manipulation protocols.